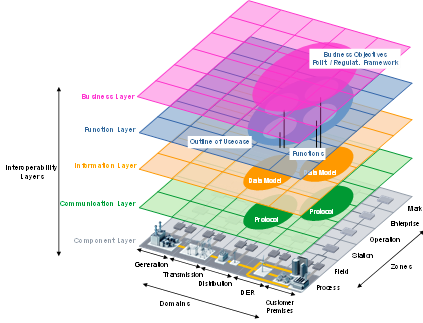
The Smart Energy Grid Architecture Model (SGAM) is a three-dimensional architectural framework described in the IEC 63200 document. This model can be used to model the exchange of information between different entities located within
the smart energy arena. The three dimensions are Domains, Zones, and Layers. Of primary interest for communication concepts are the Interoperability Layers – a slice through this 3-D model to show it more easily as two dimensions.
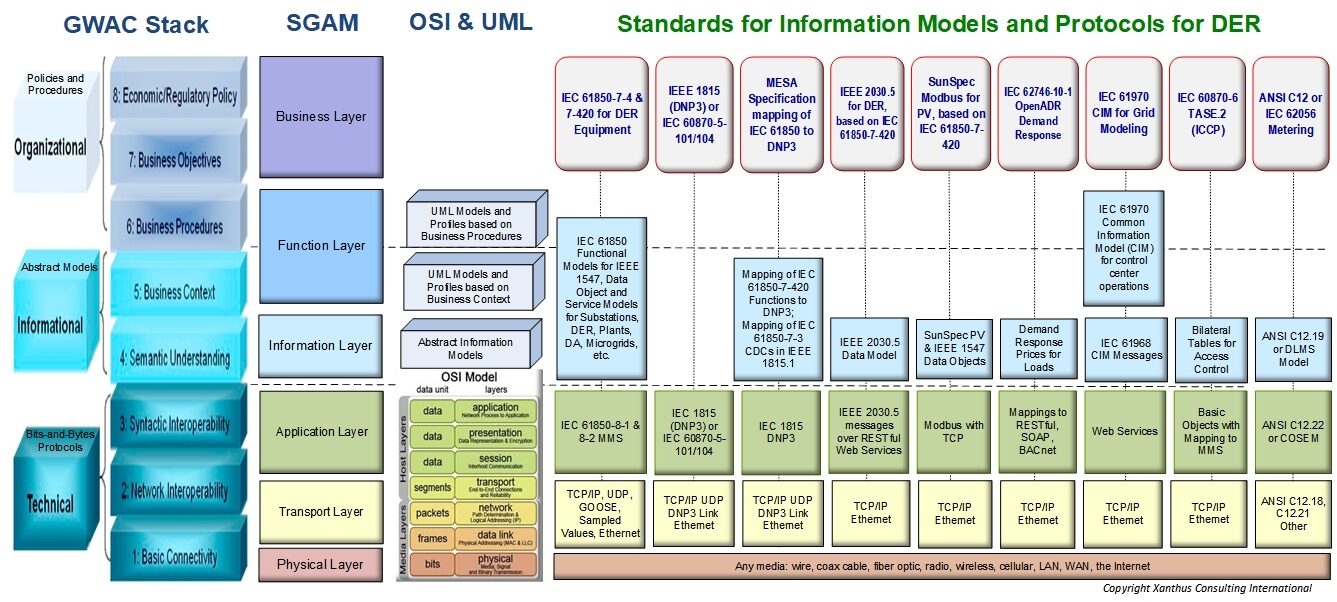
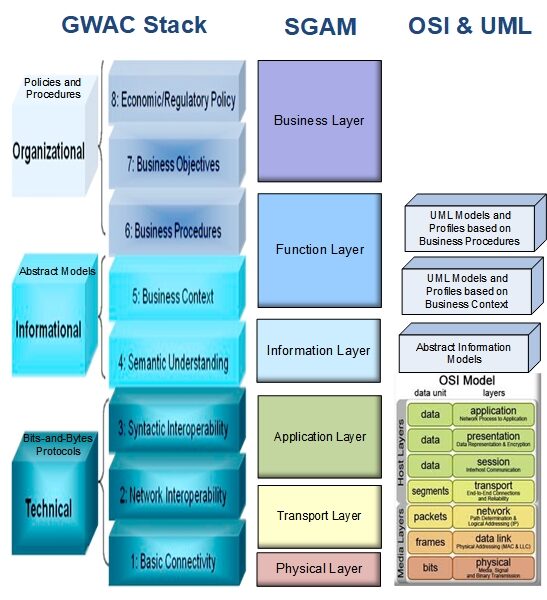
Communications involve more than the traditional concept of communication protocols (e.g. just bits and bytes going over a wire). The exchange of information involves multiple layers of interactions, involving business purposes down to the various media that could transport the information (including carrier pigeons). As an example, the GWAC Stack model and the SGAM model are different: the GWAC stack has 8 layers, while the IEC’s Smart Grid Architecture Model (SGAM) identifies 6 communication layers, but these two models were easily “mapped” to each other. The following are the primary layers:
IEC 61850-7-420 is the information model for Distributed Energy Resources, and those data objects can be mapped directly to different protocols, such as the IEC 61850-8-1 MMS protocol, the IEC 61850-8-2 XMPP protocol, the IEC 60870-5-104 (based on IEC 61850-8-1), and the IEEE 1815 (DNP3 protocol), based on the MESA Specification mapping.
IEC 61850-7-420 is also used by other protocols as a source of data objects, even though they modify the data objects to fit their protocols. Examples include IEEE 2030.5 for DER and SunSpec Modbus Specifications for DER. There are additional
efforts on “harmonizing” the Common Information Model (CIM) with the IEC 61850-7-420 to provide support for DERMS and utility Energy Management Systems.